Inspectors
Here you will find answers to the following questions:
|
1 Technical qualification requirements
The pertinent legal regulations do not stipulate any specific requirements for the inspectors in the companies who carry out self-inspections or inspections of third parties. In principle, the inspector must be employed only on the basis of his training and knowledge. This applies in particular for inspectors in the pharmaceuticals business. Inspectors must have sufficient knowledge of and experience in the area under inspection to be able to perform their task effectively. This requires an adequate, preferably academic vocational training. In addition to the technical aspects of the respective area, the inspectors must also have knowledge of the application and interpretation of the relevant legal regulations. In the field of classical pharmaceutical manufacturing of liquid, semi-solid or solid dosage forms, so-called "generalists" with an in-depth training and broad professional experience can be employed as inspectors. They check the functionality of the pharmaceutical quality assurance system as a whole. For specific areas, processes or systems (e.g. biotechnology, sterile manufacturing, computer-assisted systems, API synthesis), on the other hand, a certain level of expertise is absolutely necessary and the employment of "specialists" is essential.
Regular training is a must for inspectors. In order to be able to adequately assess the area to be inspected, the inspectors must adapt their knowledge to the scientific-technical developments and always be ready to learn about these.
For these reasons, employees in management positions with many years of professional experience are especially predestined for the role of inspector in the companies. They also have experience in personnel management and operational organisation. If there is a lack of knowledge on the methodology, this can be gained through further training seminars.
For official inspectors (supervisory officers) of the European Union, standardised EU qualification requirements are stipulated: The requirements of official inspectors are described in the Compilation of Community Procedures on Inspections and Exchange of Information (EMEA/INS/GMP/3351/03). According to this, official inspectors should in principle be able to prove that the qualified person is qualified in accordance with Article 49 of EU Directive 2001/83/EU. Objectivity, personal integrity, technical competence and the ability to audit is expected of them. Official inspectors should always be aware of their influence on operational decision-making processes. They should be ready to answer questions, but should not assume the role of consultant.
Official inspectors should be well trained in the fields of quality assurance, manufacturing processes and controls as well as sales of drugs. To be appointed as an official inspector, the above-mentioned EU document demands proof of knowledge in specific pharmaceutical specialist areas (cf. figure 18.C-2).
| Knowledge to be proven by official inspectors |
|---|
|
2 Personal requirements
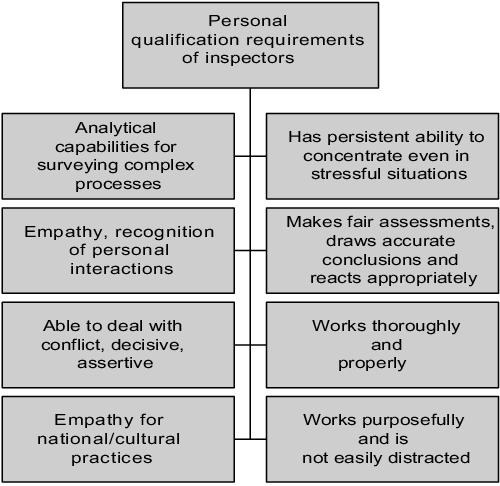
In addition to the purely technical aspects of inspector qualifications, in practice particular attention is also paid to inspectors' personal characteristics. An inspector must be able to and want to work with people. He should be able to approach them and communicate with them. He should be able to recognise personal interactions and be able to react to them adequately.
His main task during the inspection is to collect information on the basis of which he can make an assessment of the object of inspection. When procuring this information, he must proceed in a focused and purposeful manner. He must be able to quickly fit into new structures, which requires a high ability to abstract and corresponding mental flexibility. He must always be open to new ideas and be able to deal with them impartially.
An inspection can be a stressful situation for many people, both for the inspector and for the inspected. The inspector must therefore be able to work under pressure both physically and mentally.
He must not let himself be put under pressure or manipulated during his work. He must be able to argue unwaveringly and enforce a decision once made, even if this causes a conflict with the company inspected. To this extent, an inspector must also be able to enwdure conflicts. At the same time, however, he must also be able to admit when he has made the wrong decision.
Summary A requirement for qualification as an inspector is a good basic education, technical knowledge and professional experience as well as knowledge of the inspection methodology. An inspector must also be able to work under pressure both physically and mentally, and must be mentally flexible, able to communicate and be assertive and must not be easily manipulated. |